| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
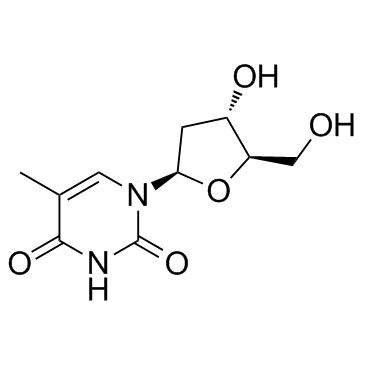 |
Thymidine
CAS:50-89-5 |
|
 |
Broxuridine
CAS:59-14-3 |
|
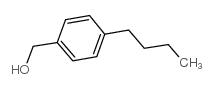 |
(4-butylphenyl)methanol
CAS:60834-63-1 |