| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Phosmet
CAS:732-11-6 |
|
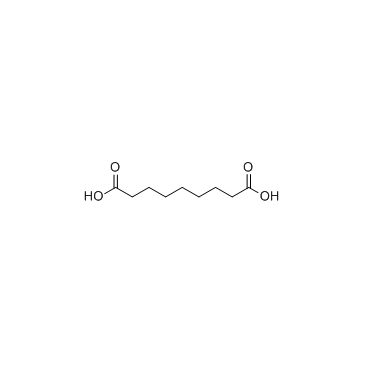 |
Azelaic acid
CAS:123-99-9 |