| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Retinoic acid
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
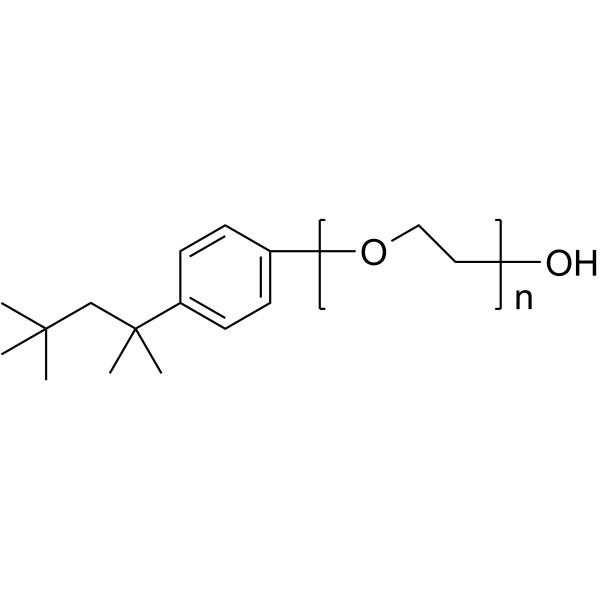 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
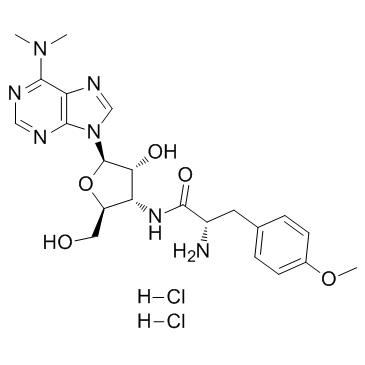 |
Puromycin 2HCl
CAS:58-58-2 |
|
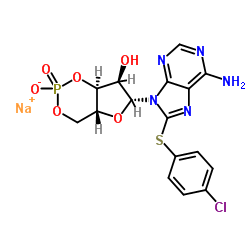 |
8-CPT-Cyclic AMP sodium
CAS:93882-12-3 |
|
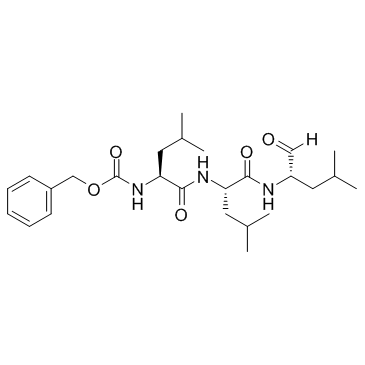 |
MG-132
CAS:133407-82-6 |
|
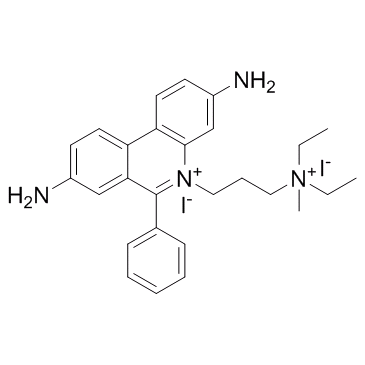 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
 |
TMRM Perchlorate
CAS:115532-50-8 |