| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
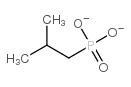 |
Isopropyl methylphosphonic acid
CAS:1832-54-8 |
|
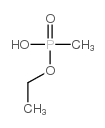 |
ETHYL METHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID
CAS:1832-53-7 |
|
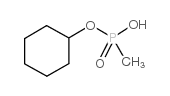 |
CYCLOHEXYL METHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID
CAS:1932-60-1 |
|
 |
Methylphosphonic acid
CAS:993-13-5 |