| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
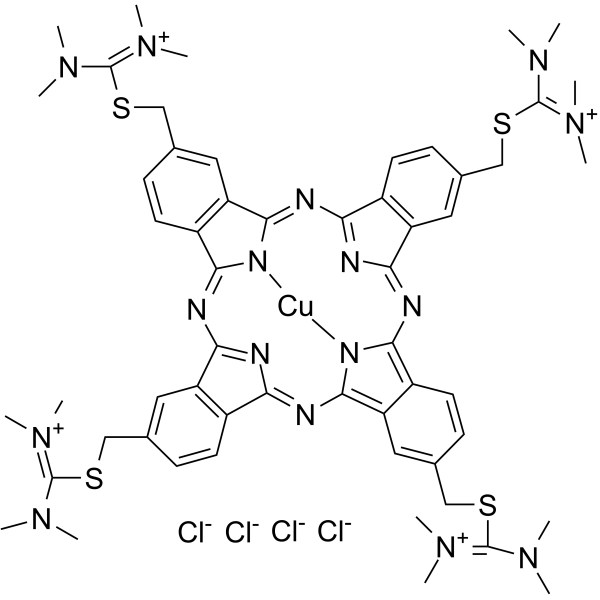 |
C.I. 74240
CAS:33864-99-2 |
|
 |
Sodium selenite
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
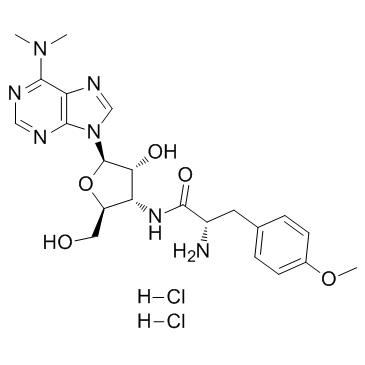 |
Puromycin 2HCl
CAS:58-58-2 |
|
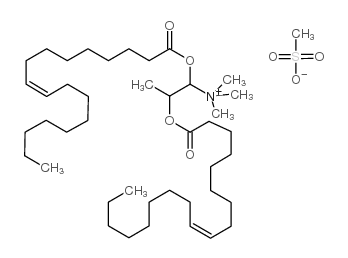 |
DOTAP Transfection Reagent
CAS:144189-73-1 |