| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
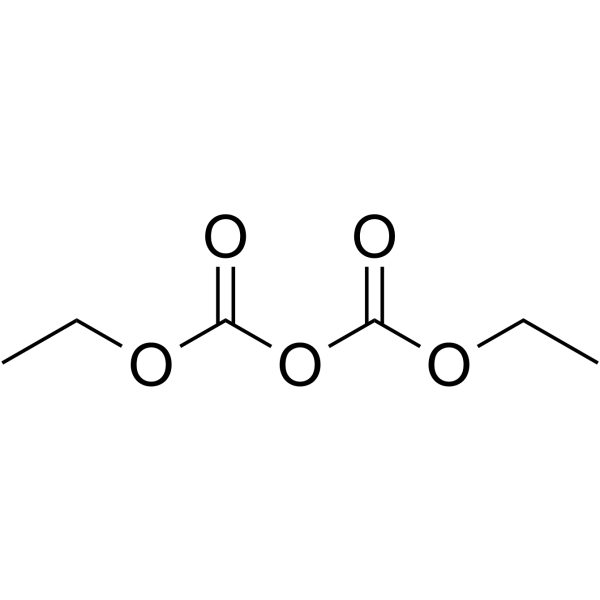 |
Diethyl pyrocarbonate
CAS:1609-47-8 |
|
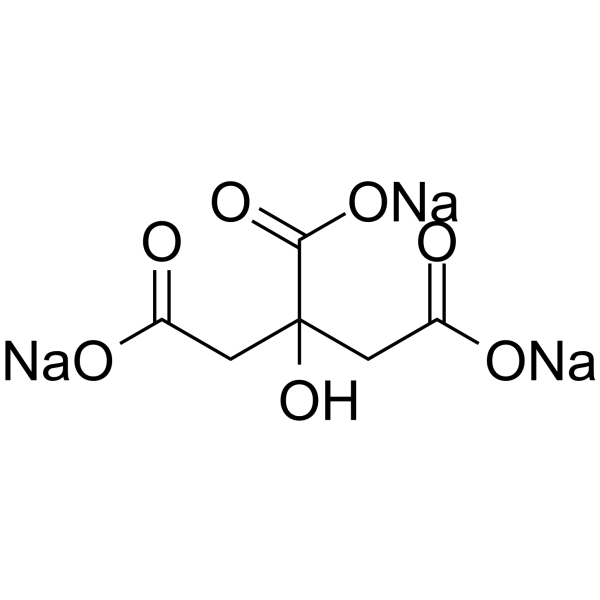 |
Sodium citrate
CAS:68-04-2 |
|
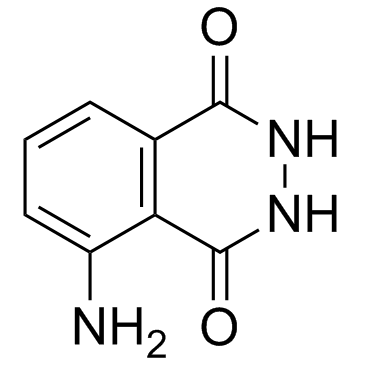 |
Luminol
CAS:521-31-3 |
|
 |
Hydrogen peroxide-urea
CAS:124-43-6 |
|
 |
Mecobalamin
CAS:13422-55-4 |