| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
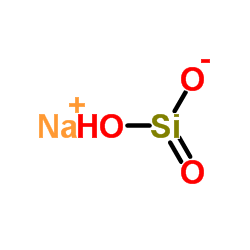 |
sodium silicate
CAS:1344-09-8 |
|
 |
Tricaprilin
CAS:538-23-8 |
|
 |
Jojoba oil
CAS:61789-91-1 |
|
 |
Cropure OL
CAS:8001-25-0 |
|
 |
Lithium
CAS:7439-93-2 |
|
 |
SODIUM METASILICATE PENTAHYDRATE
CAS:10213-79-3 |