| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
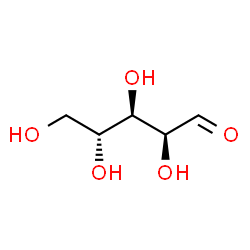 |
Pectinase
CAS:9032-75-1 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Galacturonic acid sodium salt
CAS:14984-39-5 |
|
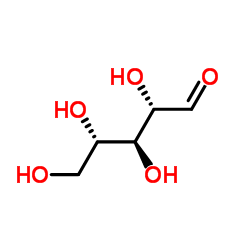 |
L-(+)-Ribose
CAS:147-81-9 |