| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
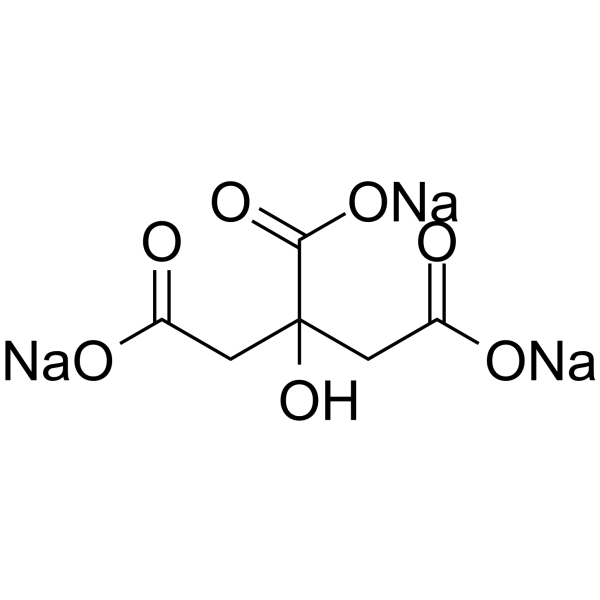 |
Sodium citrate
CAS:68-04-2 |
|
 |
N-Methyltrifluoroacetamide
CAS:815-06-5 |
|
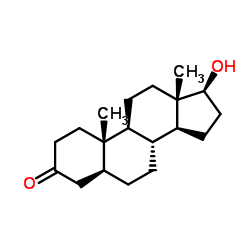 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
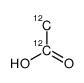 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
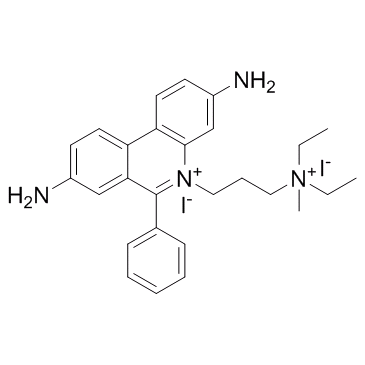 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
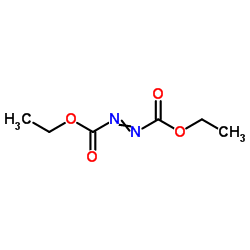 |
dead
CAS:1972-28-7 |