| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
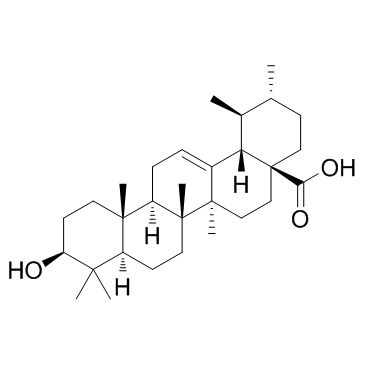 |
Ursolic Acid
CAS:77-52-1 |
|
 |
Caffeine
CAS:58-08-2 |
|
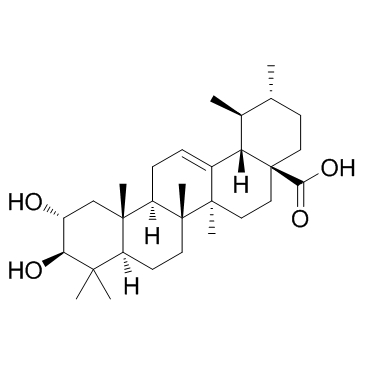 |
Corosolic acid
CAS:4547-24-4 |
|
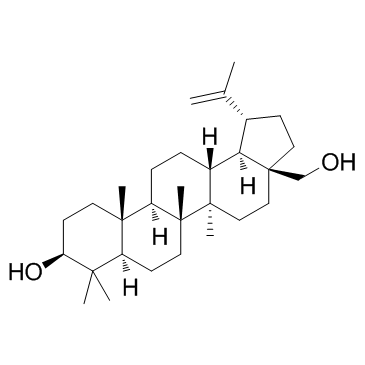 |
Betulin
CAS:473-98-3 |
|
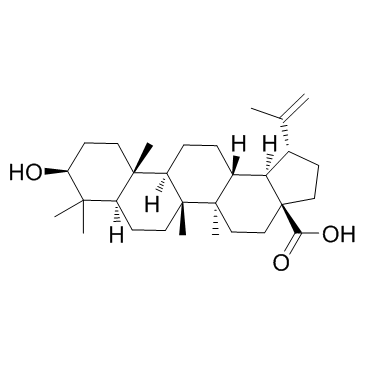 |
Betulinic acid
CAS:472-15-1 |
|
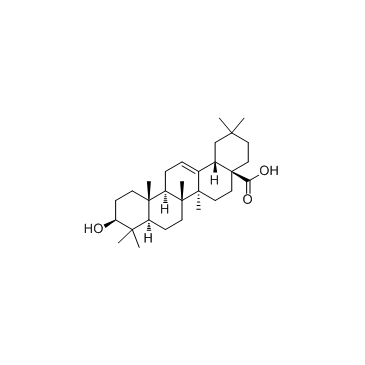 |
Oleanic acid
CAS:508-02-1 |