| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
3,6-Dichloropicolinic acid
CAS:1702-17-6 |
|
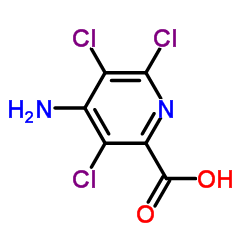 |
Picloram
CAS:1918-02-1 |
|
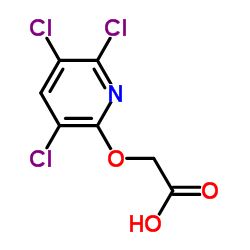 |
Triclopyr
CAS:55335-06-3 |
|
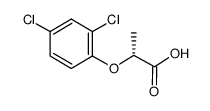 |
(R)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid
CAS:15165-67-0 |
|
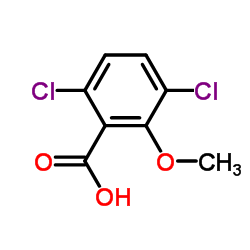 |
Dicamba
CAS:1918-00-9 |
|
 |
Dichlorprop
CAS:120-36-5 |
|
 |
2,4-Dichlorophenoxybutyric acid
CAS:94-82-6 |