| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
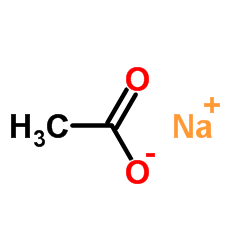 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
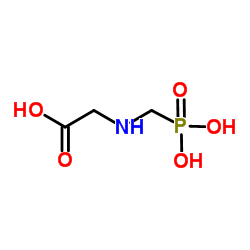 |
Glyphosate
CAS:1071-83-6 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
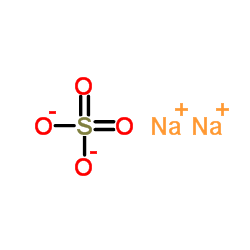 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Aqueous ammonia
CAS:1336-21-6 |
|
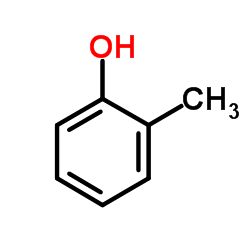 |
o-cresol
CAS:95-48-7 |
|
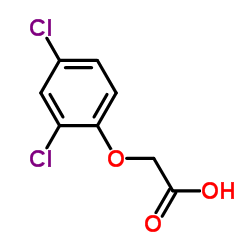 |
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
CAS:94-75-7 |
|
 |
Diazinon
CAS:333-41-5 |
|
 |
3,6-Dichloropicolinic acid
CAS:1702-17-6 |