| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
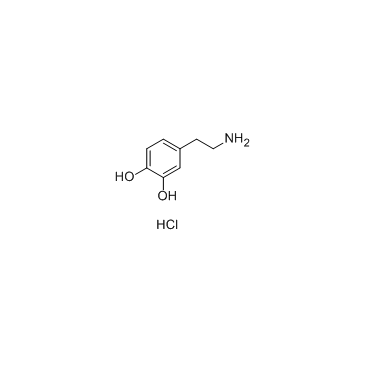 |
Dopamine hydrochloride
CAS:62-31-7 |
|
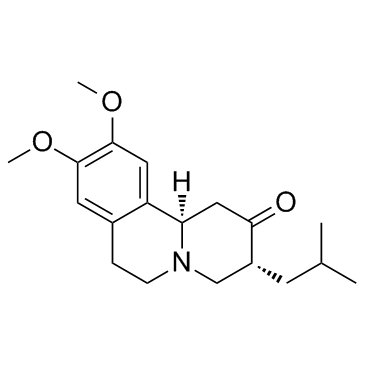 |
Tetrabenazine
CAS:58-46-8 |
|
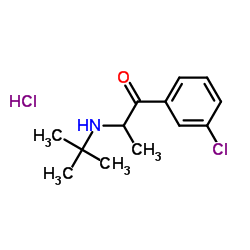 |
bupropion hydrochloride
CAS:31677-93-7 |