Adaptation of USP types II and IV controlled release assays for sparingly soluble compounds by direct eluent HPLC analysis.
P J Missel, L E Stevens
Index: Pharm. Dev. Technol. 11(1) , 87-91, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Measurement of drug release of a sparingly soluble drug by conventional methods proceeds very slowly without the aid of surfactants. Two preliminary automated methods were developed that increase sensitivity and accelerate such studies by working at very small reservoir volumes. All high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipment components were commercially available. Results are presented for the drug release of a single pellet of the sparingly soluble drug Eliprodil in two types of drug release experiments using (1) a stirred cell and (2) a flow-through method. Release rates measured from each method were comparable.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
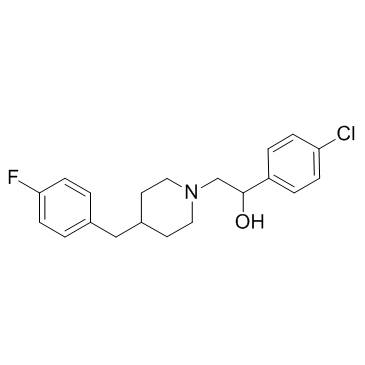 |
Eliprodil
CAS:119431-25-3 |
C20H23ClFNO |
|
NMDA receptor antagonists do not block the development of se...
2001-04-01 [Behav. Pharmacol. 12(2) , 143-9, (2001)] |
|
Synthesis and resolution of racemic eliprodil and evaluation...
2000-06-19 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 10(12) , 1377-80, (2000)] |
|
The sequential analysis of repeated binary responses: a scor...
2006-07-15 [Stat. Med. 25(13) , 2196-214, (2006)] |
|
Human retina contains polyamine sensitive [3H]-ifenprodil bi...
1999-02-01 [Br. J. Ophthalmol. 83(2) , 236-40, (1999)] |
|
Place conditioning of mice with the NMDA receptor antagonist...
1998-12-04 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 362(2-3) , 103-10, (1998)] |