| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
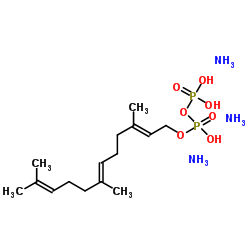 |
Farnesyl pyrophosphate
CAS:13058-04-3 |
|
 |
(E)-β-Farnesene
CAS:18794-84-8 |
|
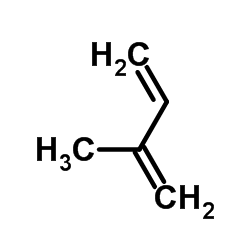 |
isoprene
CAS:78-79-5 |