| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
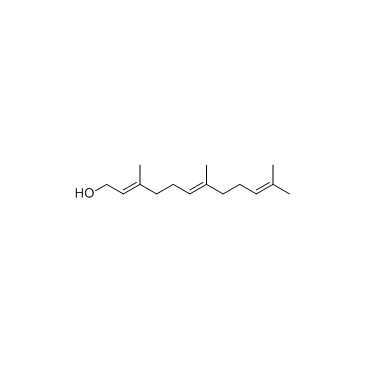 |
farnesol
CAS:4602-84-0 |
|
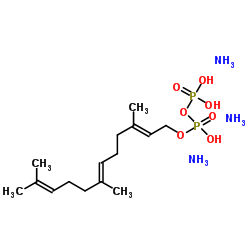 |
Farnesyl pyrophosphate
CAS:13058-04-3 |
|
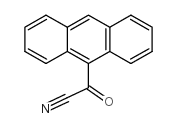 |
9-anthroylnitrile
CAS:85985-44-0 |