| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
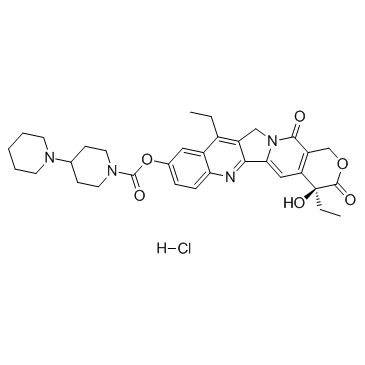 |
Irinotecan hydrochloride
CAS:100286-90-6 |
|
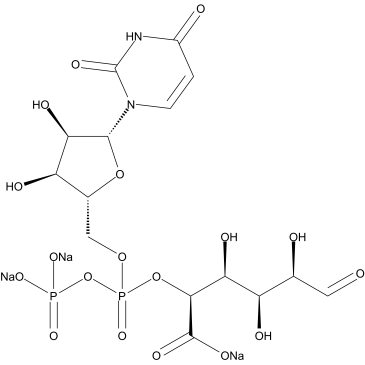 |
UDPGA
CAS:63700-19-6 |
|
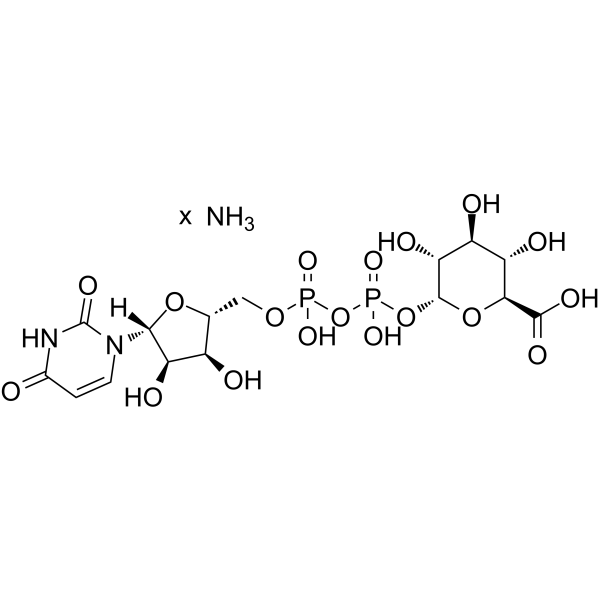 |
Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid ammonium
CAS:43195-60-4 |
|
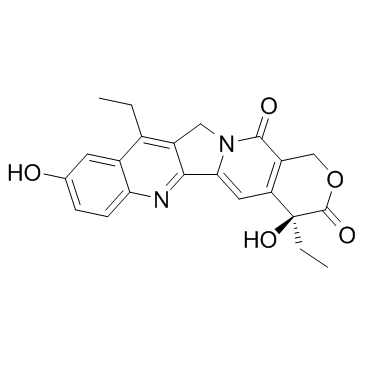 |
7-Ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin
CAS:86639-52-3 |