| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ibuprofen
CAS:15687-27-1 |
|
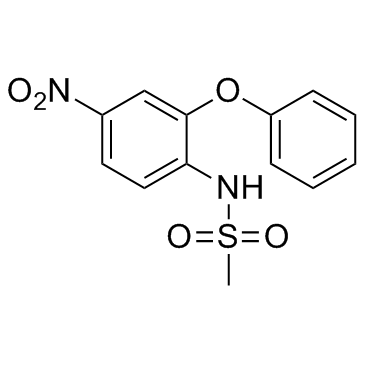 |
Nimesulide
CAS:51803-78-2 |
|
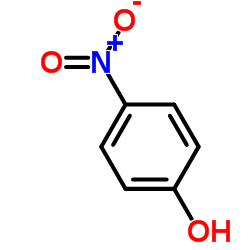 |
4-Nitrophenol
CAS:100-02-7 |
|
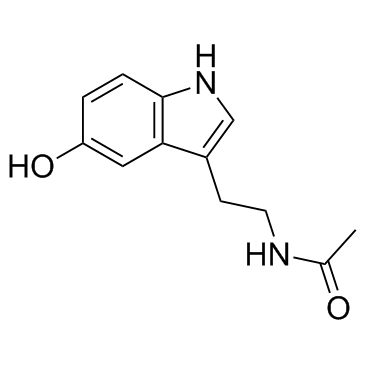 |
N-Acetylserotonin
CAS:1210-83-9 |
|
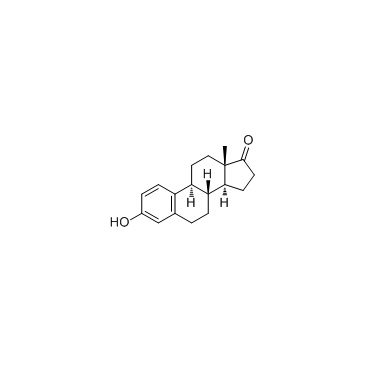 |
Estrone
CAS:53-16-7 |
|
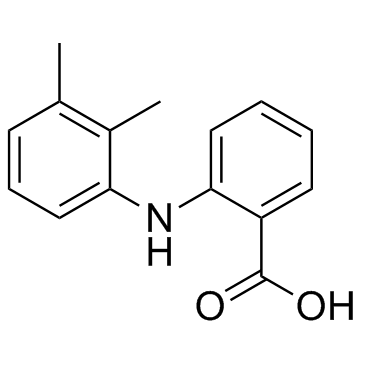 |
Mefenamic acid
CAS:61-68-7 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
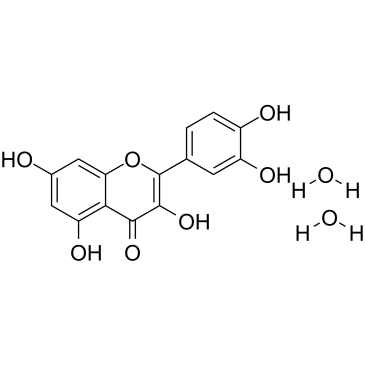 |
Quercetin dihydrate
CAS:6151-25-3 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
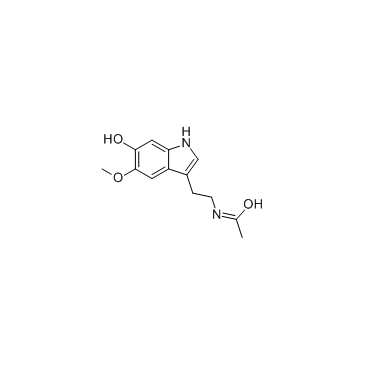 |
6-Hydroxymelatonin
CAS:2208-41-5 |