| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
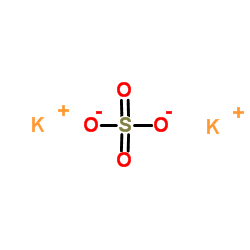 |
Potassium sulfate
CAS:7778-80-5 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
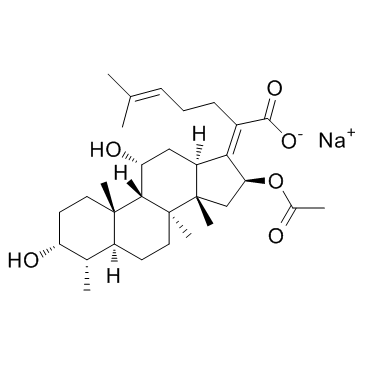 |
Fusidic acid (sodium salt)
CAS:751-94-0 |
|
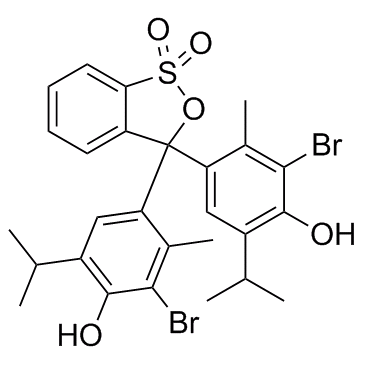 |
Bromothymol blue
CAS:76-59-5 |