| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
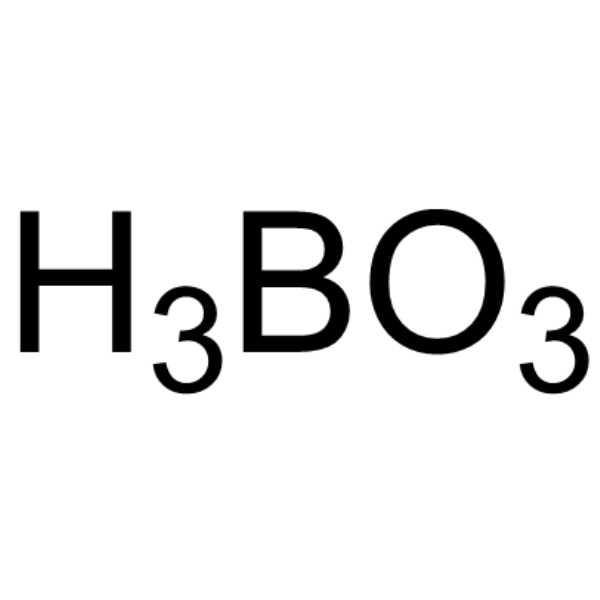 |
Orthoboric acid
CAS:10043-35-3 |
|
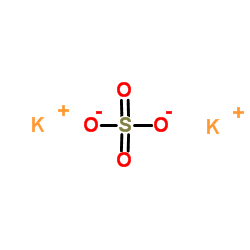 |
Potassium sulfate
CAS:7778-80-5 |
|
 |
Water
CAS:7732-18-5 |
|
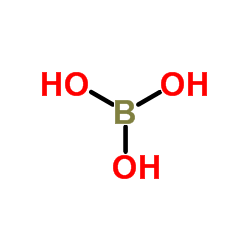 |
Boric acid-11B
CAS:13813-78-0 |