| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
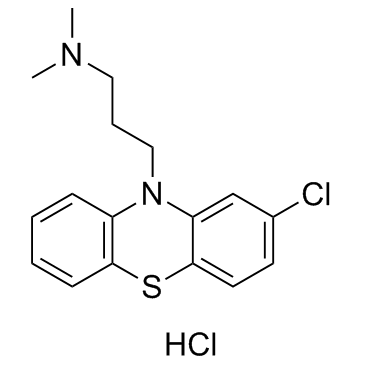 |
Chlorpromazine hydrochloride
CAS:69-09-0 |
|
 |
Calmidazolium chloride
CAS:57265-65-3 |