| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
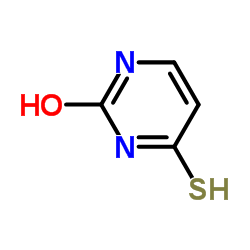 |
4-Thiouracil
CAS:591-28-6 |
|
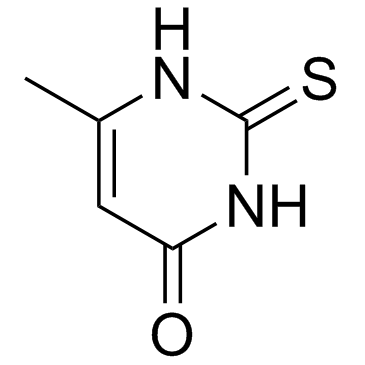 |
Methylthiouracil
CAS:56-04-2 |
|
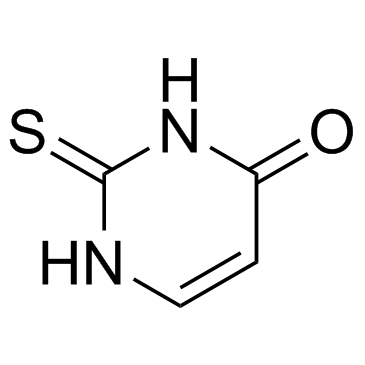 |
2-Thiouracil
CAS:141-90-2 |