| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
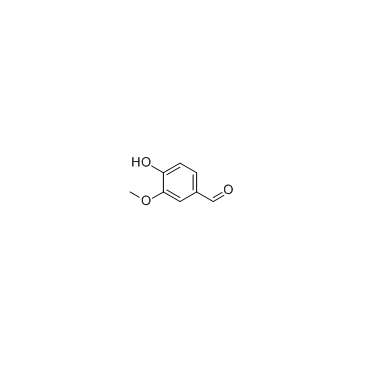 |
Vanillin
CAS:121-33-5 |
|
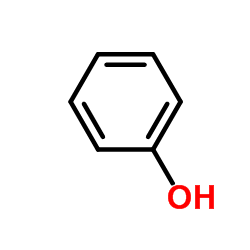 |
Phenol
CAS:108-95-2 |
|
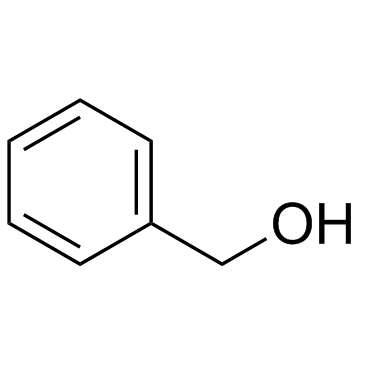 |
Benzyl alcohol
CAS:100-51-6 |
|
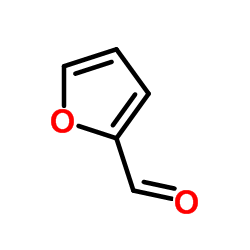 |
Furfural
CAS:98-01-1 |
|
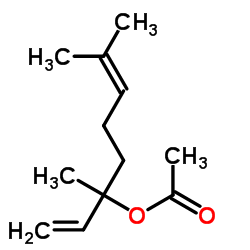 |
Linalyl acetate
CAS:115-95-7 |
|
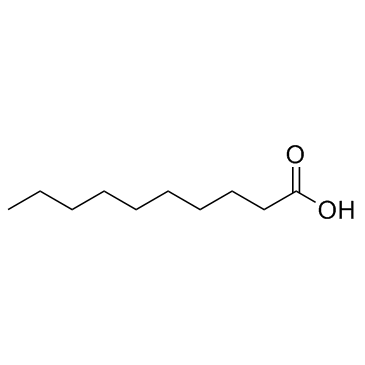 |
Decanoic acid
CAS:334-48-5 |
|
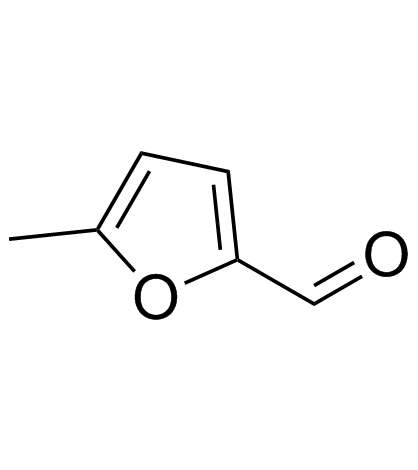 |
5-Methyl-2-furaldehyde
CAS:620-02-0 |
|
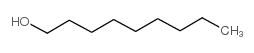 |
1-Nonanol
CAS:143-08-8 |
|
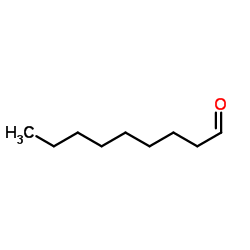 |
Nonanal
CAS:124-19-6 |
|
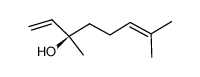 |
(-)-Linalool
CAS:126-91-0 |