Liquid chromatographic properties and aqueous solution stability of N-hydroxy-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine.
A K Valaer, W R Ravis, C R Clark
Index: J. Chromatogr. Sci. 28 , 482, (1990)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The reversed-phase liquid chromatographic properties of N-hydroxy-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (NOHMDA) were determined on a C8 stationary phase specifically prepared for the separation of basic compounds. NOHMDA and several N-alkyl MDA derivatives displayed excellent peak shape on this stationary phase without the need for competing bases such as triethylamine. The k' values for NOHMDA varied with mobile phase pH in the range of 2.5 to 6.0, but the retention of the primary amine, MDA, and N-alkyl MDAs remained relatively constant over this range. The pKa value for NOHMDA was determined by titration to be 6.22 compared to a pKa of 10.04 for MDA. Thus, the variation of k' with mobile phase pH for NOHMDA may be a result of appreciable changes in degree of protonation. The stability of NOHMDA was found to decrease with an increase in aqueous solution pH. At pH 7.0 the degradation half-life was determined to be 49.8 h, which decreased to 2.57 h at pH 10.0. Above pH 10.0 the decomposition to the corresponding oxime was too fast for a reliable half-life determination.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
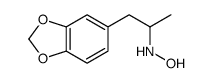 |
(+/-)-n-hydroxy-3 4-methylenedioxyamphe&
CAS:114562-59-3 |
C10H13NO3 |
|
[Studies on the identification of psychotropic substances. I...
1993-01-01 [Eisei Shikenjo Hokoku. (111) , 66-74, (1993)] |
|
In vivo formation of aromatic hydroxylated metabolites of 3,...
1991-11-01 [Biol. Mass Spectrom. 20(11) , 677-86, (1991)] |
|
Stimulus effects of N-monoethyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)...
1989-08-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 33(4) , 909-12, (1989)] |
|
Determination of a new designer drug, N-hydroxy-3,4-methylen...
2010-05-20 [Forensic Sci. Int. 198(1-3) , 62-9, (2010)] |
|
The pharmacokinetics and liver metabolism of N-hydroxy-3,4-m...
1994-01-01 [Life Sci. 54(26) , PL519-24, (1994)] |