| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
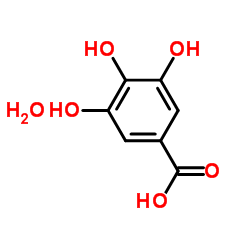 |
Gallic acid hydrate
CAS:5995-86-8 |
|
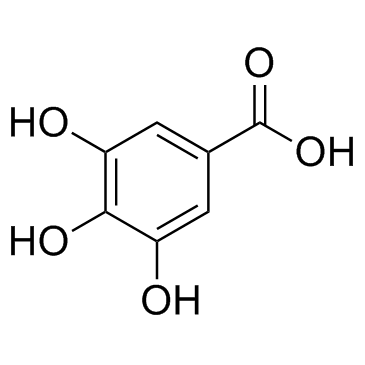 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
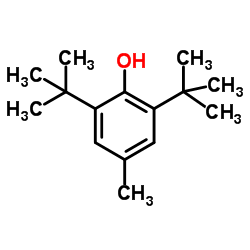 |
Butylated hydroxytoluene
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
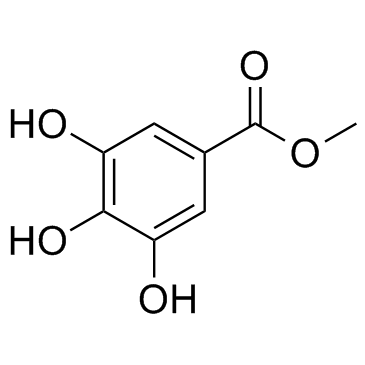 |
Methyl gallate
CAS:99-24-1 |