| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
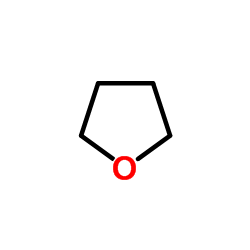 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
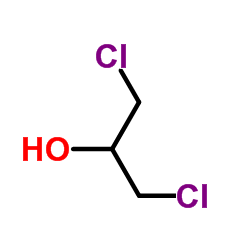 |
1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol
CAS:96-23-1 |
|
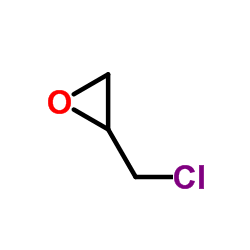 |
Epichlorohydrin
CAS:106-89-8 |