| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
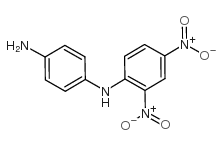 |
DISPERSE YELLOW 9
CAS:6373-73-5 |
|
 |
disperse blue 1
CAS:2475-45-8 |
|
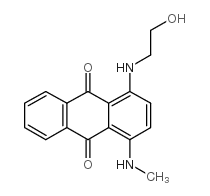 |
C.I. Disperse Blue 3
CAS:2475-46-9 |
|
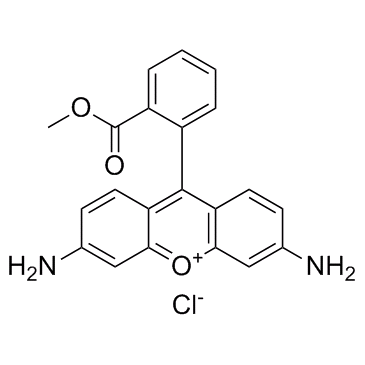 |
Rhodamine 123
CAS:62669-70-9 |
|
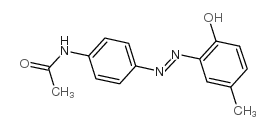 |
Disperse Yellow 3
CAS:2832-40-8 |
|
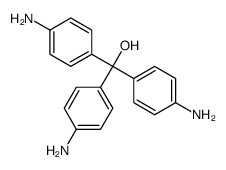 |
ci 42500
CAS:467-62-9 |
|
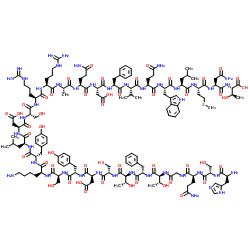 |
glucagonTFA
CAS:16941-32-5 |
|
 |
Acrylic acid
CAS:79-10-7 |
|
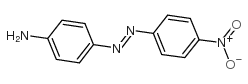 |
disperse orange 3
CAS:730-40-5 |
|
 |
Reactive Blue 19
CAS:2580-78-1 |