| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
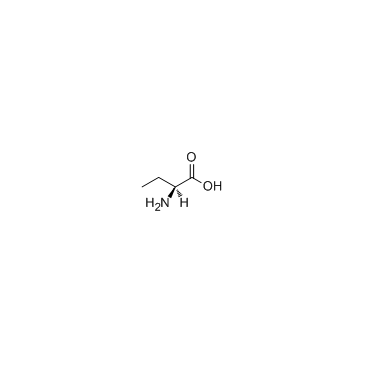 |
L(+)-2-Aminobutyric acid
CAS:1492-24-6 |
|
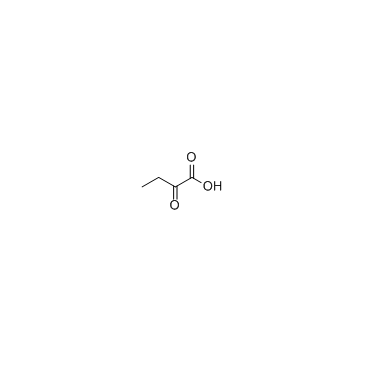 |
2-Oxobutyric acid
CAS:600-18-0 |
|
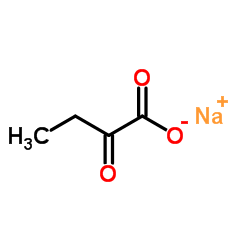 |
Sodium 2-oxobutanoate
CAS:2013-26-5 |
|
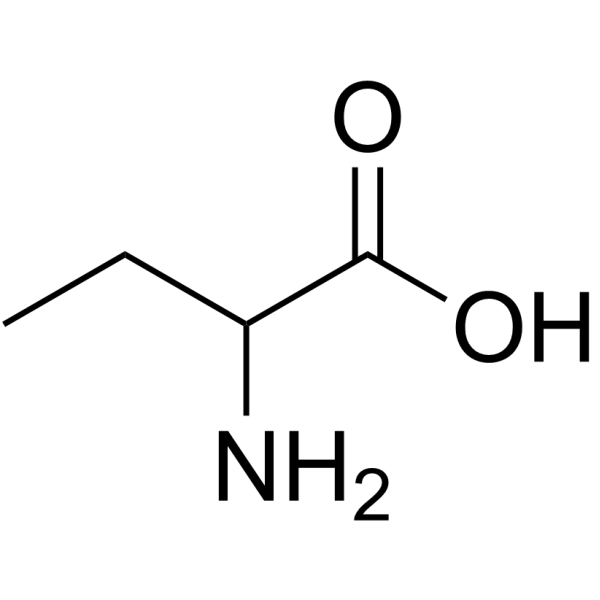 |
2-Aminobutanoic acid
CAS:2835-81-6 |
|
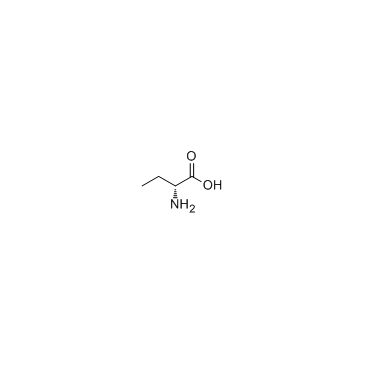 |
H-D-Abu-OH
CAS:2623-91-8 |