| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Native Bovine Alkaline Phosphatase
CAS:9001-78-9 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
Thrombin
CAS:9002-04-4 |
|
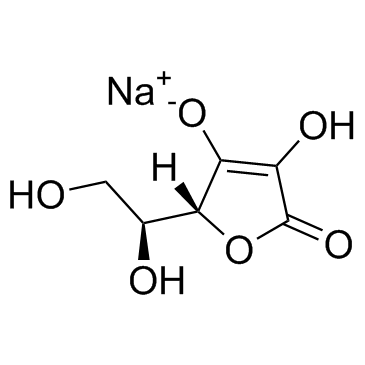 |
sodium ascorbate
CAS:134-03-2 |