| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
 |
D-(-)-Morphine
CAS:57-27-2 |
|
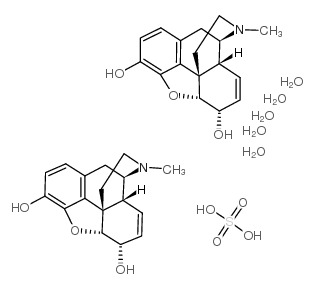 |
morphine sulfate pentahydrate
CAS:6211-15-0 |
|
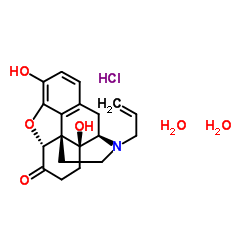 |
Naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate
CAS:51481-60-8 |
|
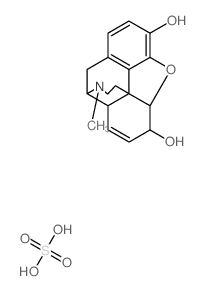 |
morphine sulfate
CAS:64-31-3 |