| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
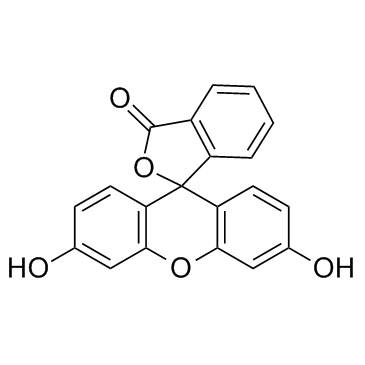 |
Fluorescein
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
 |
Luteolin-6-C-glucoside
CAS:4261-42-1 |
|
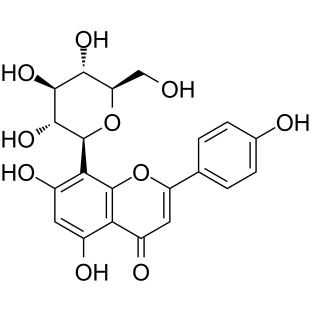 |
vitexin
CAS:3681-93-4 |
|
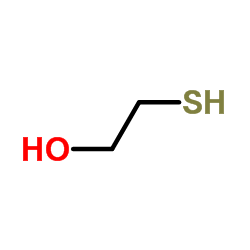 |
mercaptoethanol
CAS:60-24-2 |
|
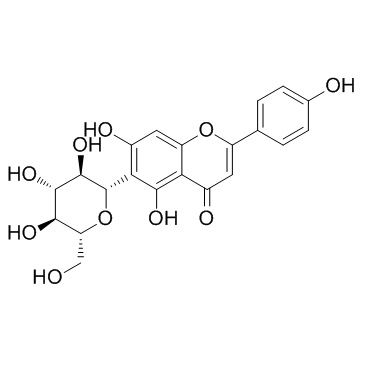 |
Isovitexin
CAS:38953-85-4 |