| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
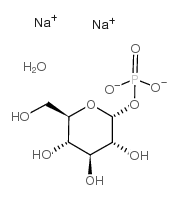 |
alpha-d-glucose-1-phosphate na2-salt
CAS:56401-20-8 |
|
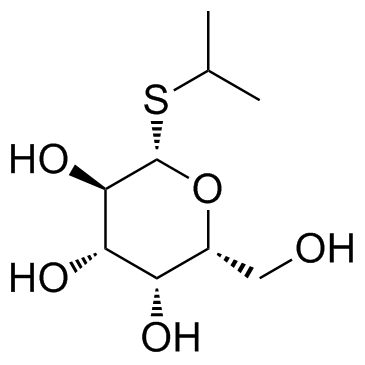 |
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside
CAS:367-93-1 |
|
 |
L-cysteine
CAS:52-90-4 |
|
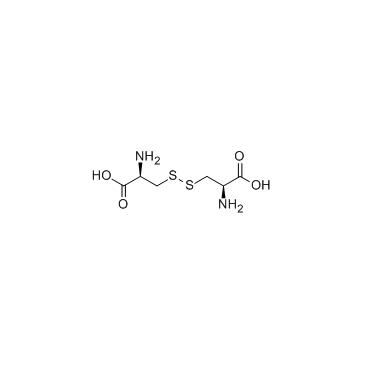 |
L-Cystine
CAS:56-89-3 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
Uridine-5'-diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase
CAS:9026-22-6 |
|
 |
Thioredoxin, from Escherichia coli
CAS:52500-60-4 |
|
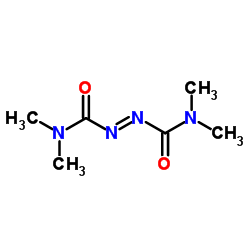 |
N,N,N',N'-Tetramethylazodicarboxamide
CAS:10465-78-8 |
|
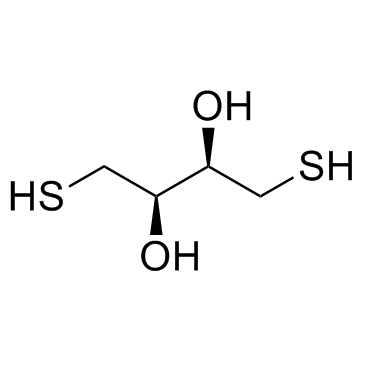 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |