| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine)
CAS:616-91-1 |
|
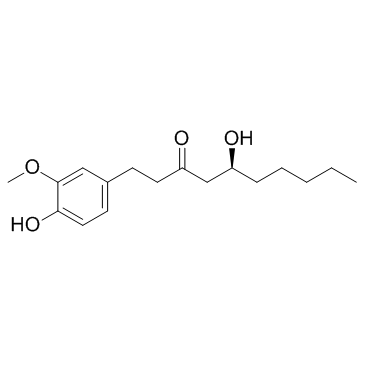 |
6-Gingerol
CAS:23513-14-6 |