| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
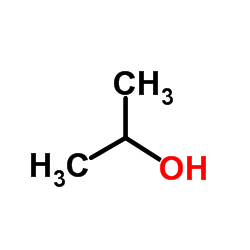 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
HEPES sodium salt
CAS:75277-39-3 |
|
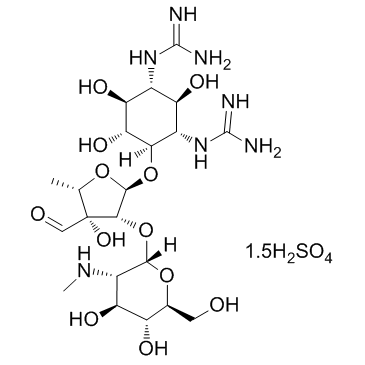 |
Steptomycin sulfate
CAS:3810-74-0 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
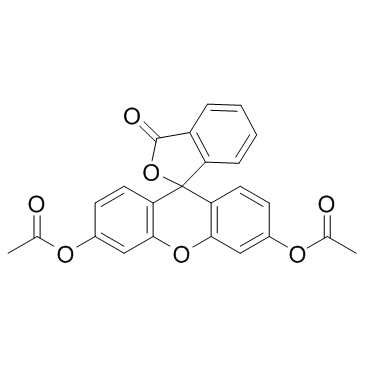 |
Fluorescein Diacetate
CAS:596-09-8 |