| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Selenium
CAS:7782-49-2 |
|
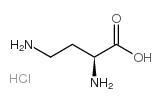 |
H-Dab.HCl
CAS:1482-98-0 |
|
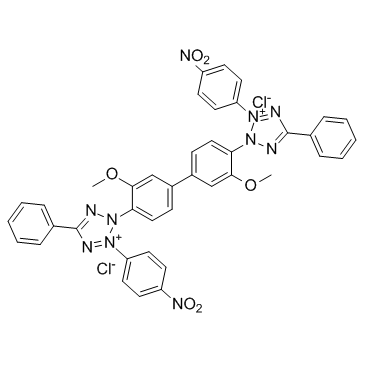 |
NBT
CAS:298-83-9 |
|
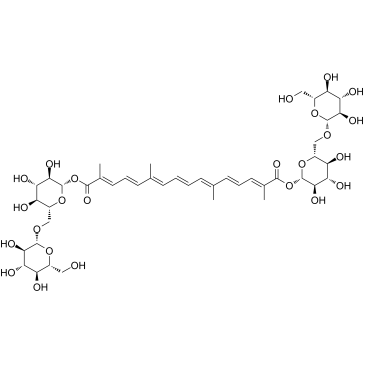 |
Crocin
CAS:42553-65-1 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |