| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
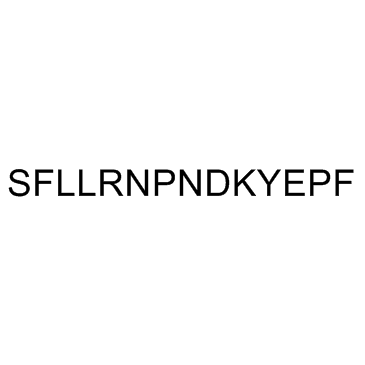 |
TRAP-14 trifluoroacetate salt
CAS:137339-65-2 |
|
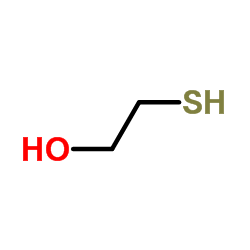 |
mercaptoethanol
CAS:60-24-2 |
|
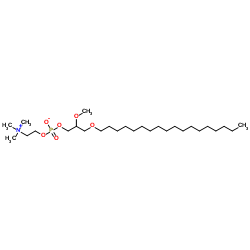 |
Edelfosine
CAS:70641-51-9 |
|
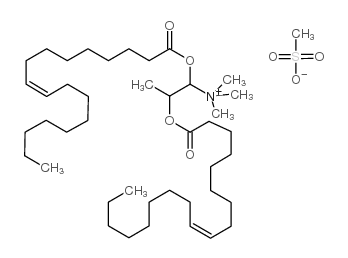 |
DOTAP Transfection Reagent
CAS:144189-73-1 |
|
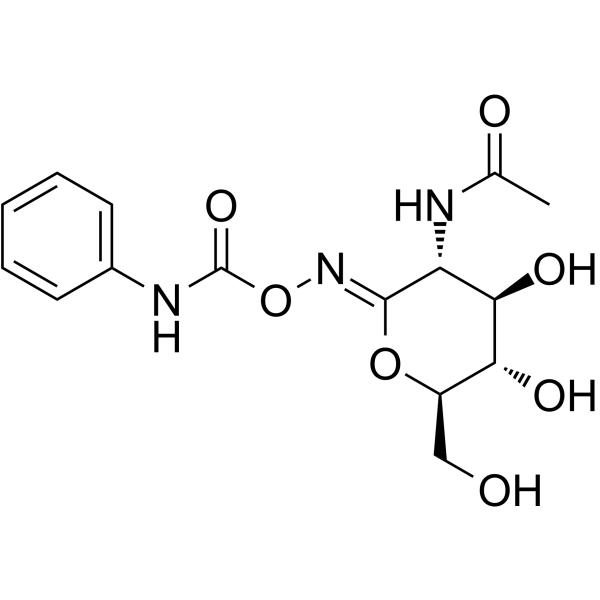 |
PugNAc
CAS:132489-69-1 |