| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Propofol
CAS:2078-54-8 |
|
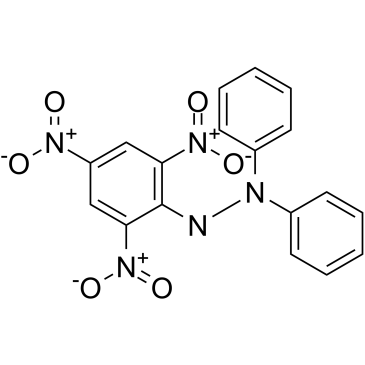 |
DPPH
CAS:1898-66-4 |
|
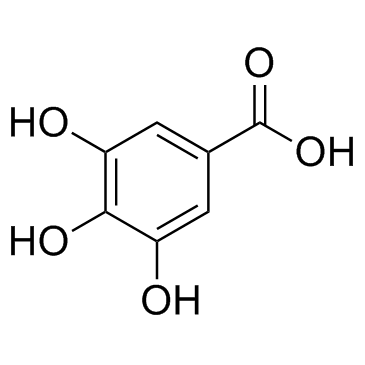 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
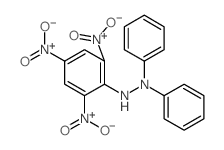 |
1,1-DIPHENYL-2-PICRYLHYDRAZINE
CAS:1707-75-1 |
|
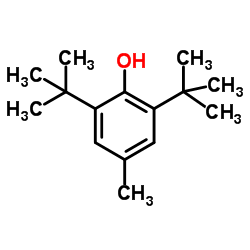 |
Butylated hydroxytoluene
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
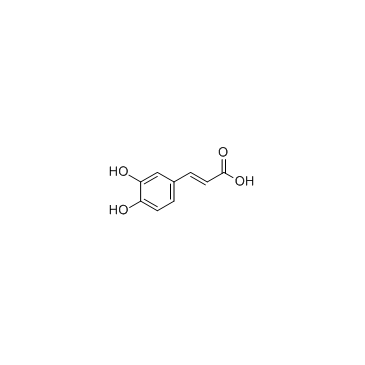 |
Caffeic acid
CAS:331-39-5 |
|
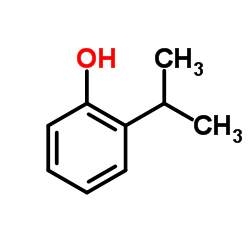 |
o-nitroaniline
CAS:88-69-7 |
|
 |
2-tert-Butyl-4-methoxyphenol
CAS:121-00-6 |
|
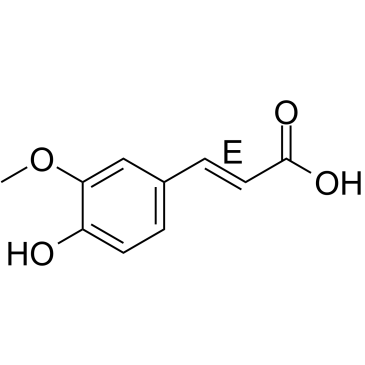 |
(E)-Ferulic acid
CAS:537-98-4 |