| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
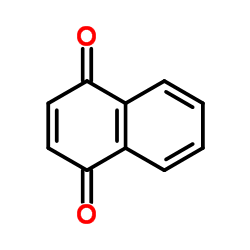 |
1,4-naphthoquinone
CAS:130-15-4 |
|
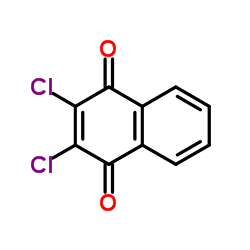 |
2,3-Dichlor-1,4-naphthochinone
CAS:117-80-6 |
|
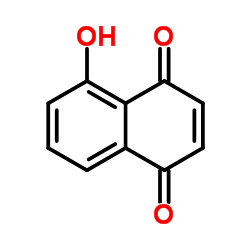 |
Juglone
CAS:481-39-0 |
|
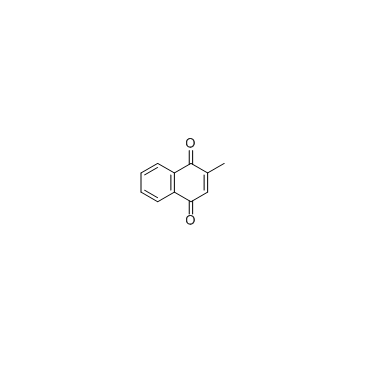 |
Menadione
CAS:58-27-5 |