| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
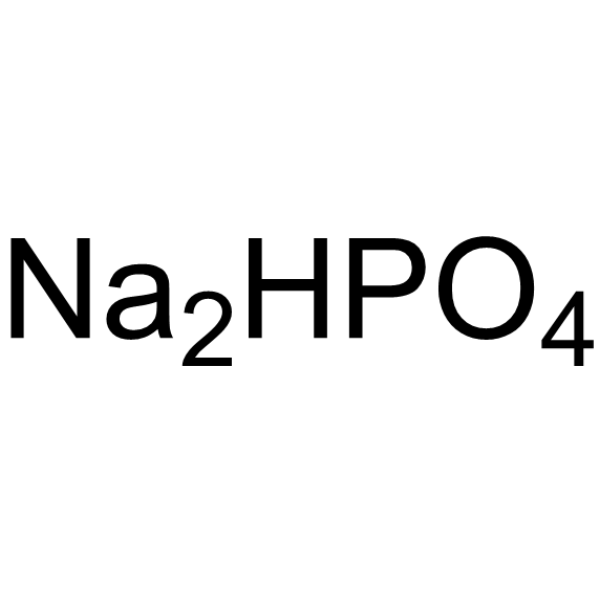 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
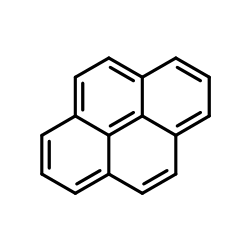 |
Pyrene
CAS:129-00-0 |
|
 |
sodium dihydrogenphosphate
CAS:7558-80-7 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
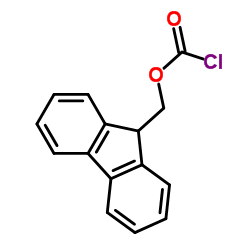 |
9-Fluorenylmethyl chloroformate
CAS:28920-43-6 |
|
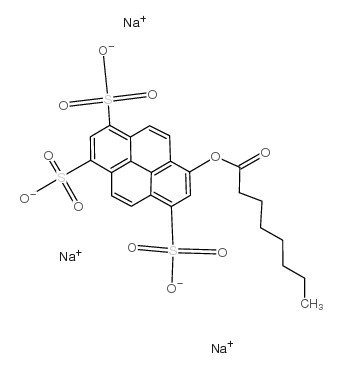 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |