| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
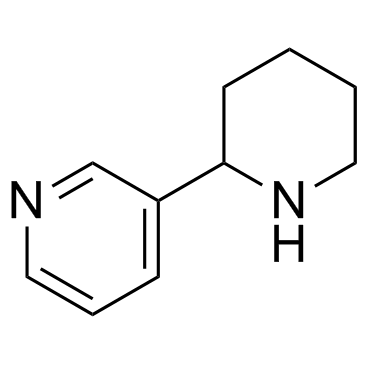 |
(±)-Anabasine
CAS:13078-04-1 |
|
 |
L-Nicotine
CAS:54-11-5 |
|
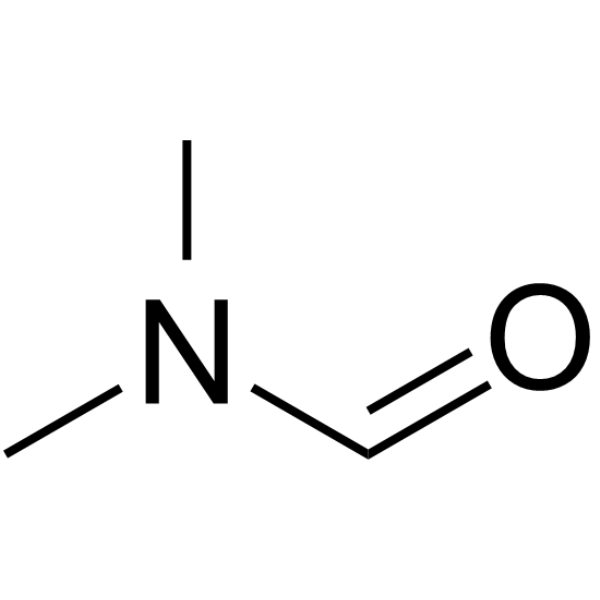 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
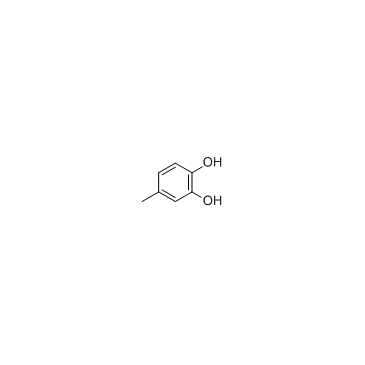 |
4-methylcatechol
CAS:452-86-8 |
|
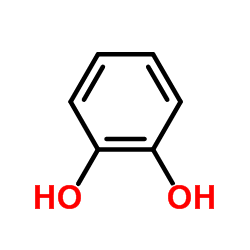 |
1,2-Benzenediol
CAS:120-80-9 |
|
 |
trans,trans-Muconic Acid
CAS:3588-17-8 |