| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
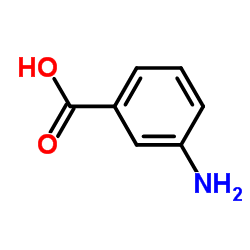 |
3-Aminobenzoic acid
CAS:99-05-8 |
|
 |
3-Methoxybenzoic acid
CAS:586-38-9 |
|
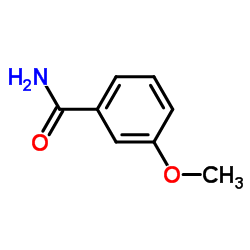 |
3-Methoxybenzamide
CAS:5813-86-5 |