ACE inhibition by astilbin isolated from Erythroxylum gonocladum (Mart.) O.E. Schulz.
M D Lucas-Filho, G C Silva, S F Cortes, T R Mares-Guia, V Perpétua Ferraz, C P Serra, F C Braga
Index: Phytomedicine 17(5) , 383-7, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Erythroxylum species have several traditional uses in different countries, including the treatment of hypertension. The ethanol extract from E. gonocladum aerial parts, a species endemic to the Brazilian cerrado, elicited a concentration-dependent inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) (pIC(50)=4.53+/-0.05). Extract fractionation led to the isolation of two compounds, whose structures were assigned by spectrometric data as astilbin and beta-sitosterol, along with a mixture of palmitic, stearic and linolenic acids. This is the first report on the occurrence of these compounds on E. gonocladum. Astilbin promoted significant ACE inhibition in vitro (pIC(50)=5.86+/-0.33) and its activity did not differ from captopril, when both compounds were assayed at 10 microM concentration.Copyright 2009 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
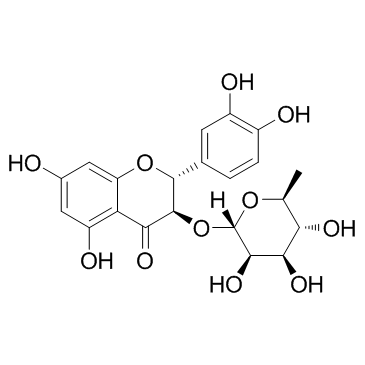 |
Astilbin
CAS:29838-67-3 |
C21H22O11 |
|
Isolation and characterization of two flavonoids, engeletin ...
2011-05-11 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(9) , 4562-9, (2011)] |
|
Chemical constituents comparison between Rhizoma Smilacis Gl...
2013-01-01 [Nat. Prod. Res. 27(3) , 277-81, (2013)] |
|
Induction of TGF-_ and IL-10 production in dendritic cells u...
2014-04-01 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 446(2) , 529-34, (2014)] |
|
Effect of astilbin on experimental diabetic nephropathy in v...
2009-11-01 [Planta Med. 75(14) , 1470-5, (2009)] |
|
Development of HPLC fingerprint for species differentiation ...
2013-01-01 [J. Nat. Med. 67(1) , 207-11, (2013)] |