Isolation and characterization of two flavonoids, engeletin and astilbin, from the leaves of Engelhardia roxburghiana and their potential anti-inflammatory properties.
Haiqiu Huang, Zhihong Cheng, Haiming Shi, Wenbo Xin, Thomas T Y Wang, Liangli Lucy Yu
Index: J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(9) , 4562-9, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Engeletin, a flavonoid compound, was isolated from the leaves of Engelhardia roxburghiana for the first time, along with astilbin, another flavonoid. The chemical structures of engeletin and astilbin were confirmed by (1)H and (13)C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) spectra, and their anti-inflammatory activities were studied in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated mouse J774A.1 macrophage cells. LPS induced the inflammatory state in macrophage cells and increased mRNA expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Engeletin and astilbin exhibited remarkable inhibitory effects on interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 mRNA expression. Significant inhibition of LPS-mediated mRNA expressions were also seen in LPS binding toll-like receptor (TLR)-4, pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-10, chemoattractant monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1, and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 genes. The reduced expression of these cytokines may alleviate immune response and reduce inflammatory activation, indicating that engeletin and astilbin may serve as potential anti-inflammatory agents.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
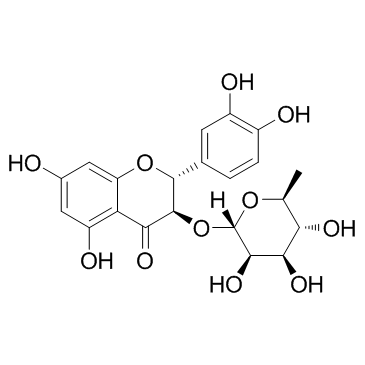 |
Astilbin
CAS:29838-67-3 |
C21H22O11 |
|
ACE inhibition by astilbin isolated from Erythroxylum gonocl...
2010-04-01 [Phytomedicine 17(5) , 383-7, (2010)] |
|
Chemical constituents comparison between Rhizoma Smilacis Gl...
2013-01-01 [Nat. Prod. Res. 27(3) , 277-81, (2013)] |
|
Induction of TGF-_ and IL-10 production in dendritic cells u...
2014-04-01 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 446(2) , 529-34, (2014)] |
|
Effect of astilbin on experimental diabetic nephropathy in v...
2009-11-01 [Planta Med. 75(14) , 1470-5, (2009)] |
|
Development of HPLC fingerprint for species differentiation ...
2013-01-01 [J. Nat. Med. 67(1) , 207-11, (2013)] |