| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
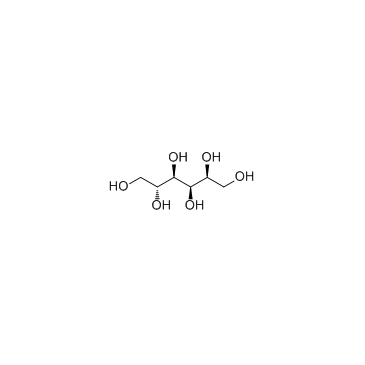 |
Sorbitol
CAS:50-70-4 |
|
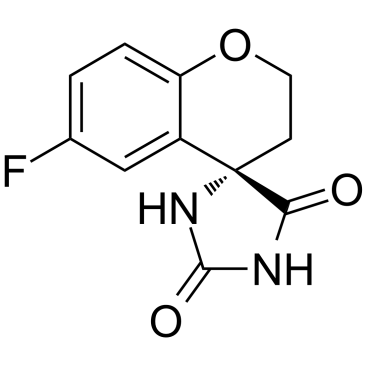 |
Sorbinil
CAS:68367-52-2 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
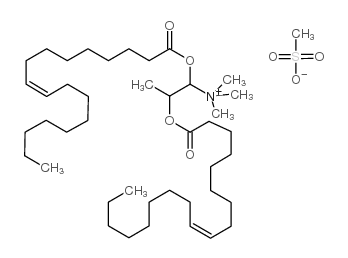 |
DOTAP Transfection Reagent
CAS:144189-73-1 |