| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
4-Aminobutanoic acid
CAS:56-12-2 |
|
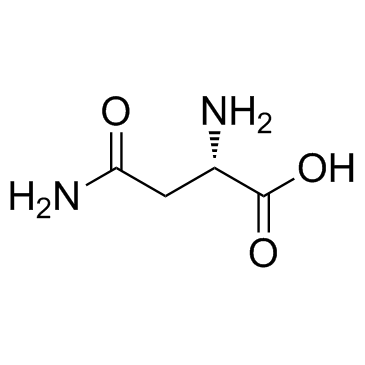 |
L-asparagine
CAS:70-47-3 |
|
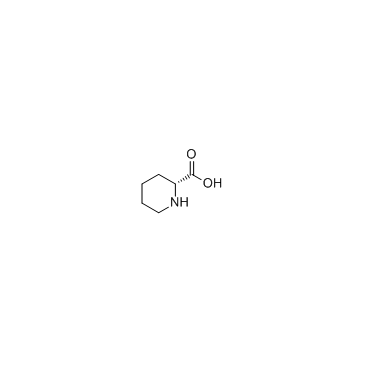 |
H-D-HomoPhe-OH
CAS:1723-00-8 |
|
 |
Isovaleraldehyde
CAS:590-86-3 |
|
 |
2-Heptanone
CAS:110-43-0 |