| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
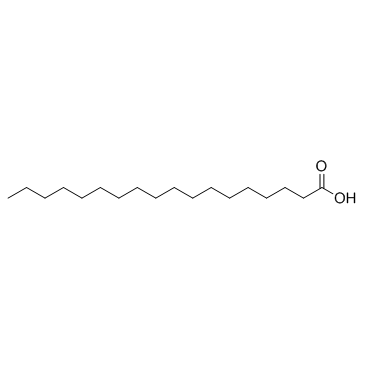 |
stearic acid
CAS:57-11-4 |
|
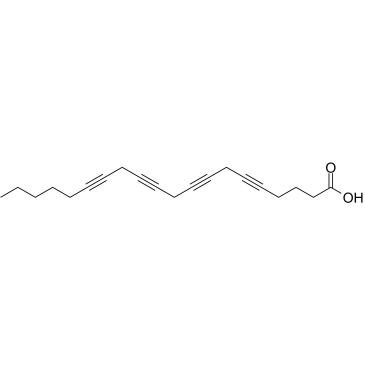 |
5,8,11,14-Icosatetraynoic acid
CAS:1191-85-1 |
|
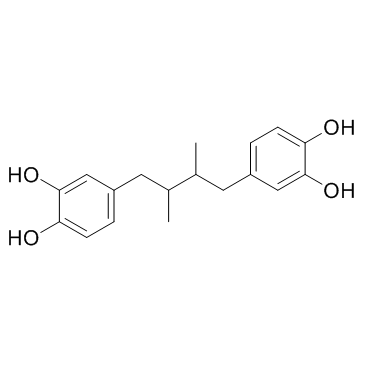 |
Nordihydroguaiaretic acid
CAS:500-38-9 |
|
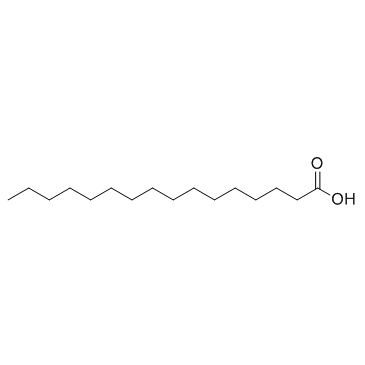 |
Palmitic acid
CAS:57-10-3 |
|
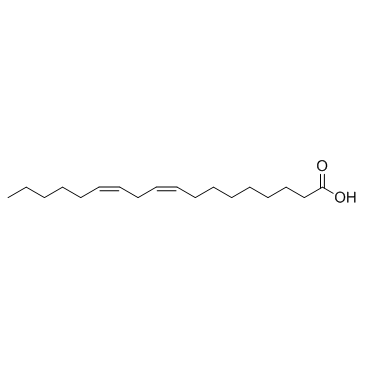 |
Linoleic acid
CAS:60-33-3 |
|
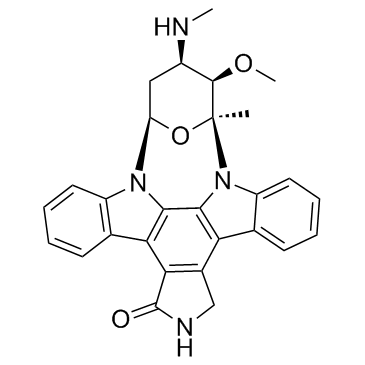 |
Staurosporine
CAS:62996-74-1 |
|
 |
oleic acid
CAS:112-80-1 |
|
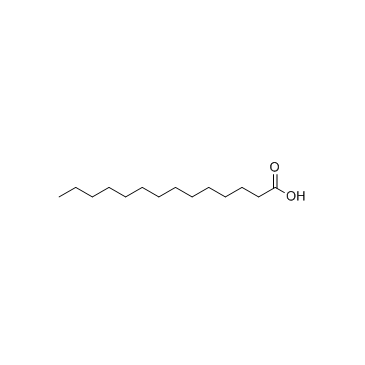 |
Myristic acid
CAS:544-63-8 |
|
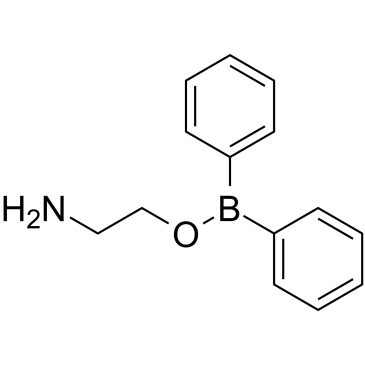 |
2-Aminoethyl Diphenylborinate
CAS:524-95-8 |