| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
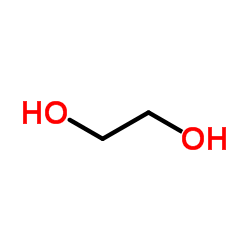 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
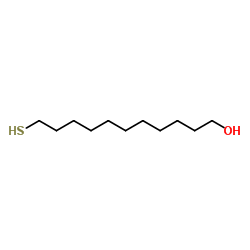 |
11-mercaptoundecanol
CAS:73768-94-2 |
|
 |
(Rac)-Golgicide A
CAS:1005036-73-6 |