| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
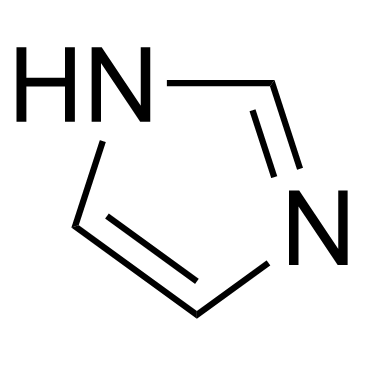 |
Imidazole
CAS:288-32-4 |
|
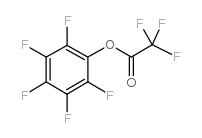 |
PENTAFLUOROPHENYL TRIFLUOROACETATE
CAS:14533-84-7 |
|
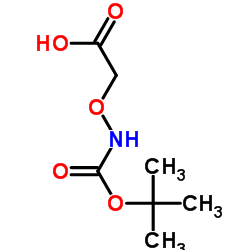 |
(Boc-aminooxy)acetic Acid
CAS:42989-85-5 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
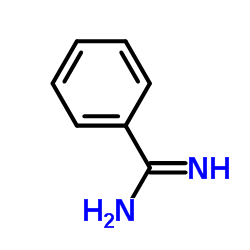 |
Benzamidine
CAS:618-39-3 |
|
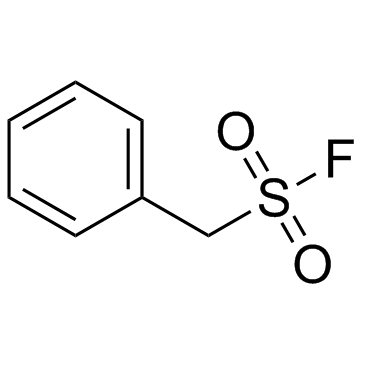 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
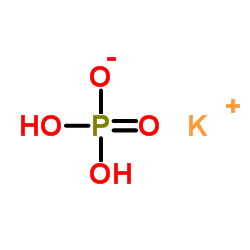 |
Monopotassium phosphate
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
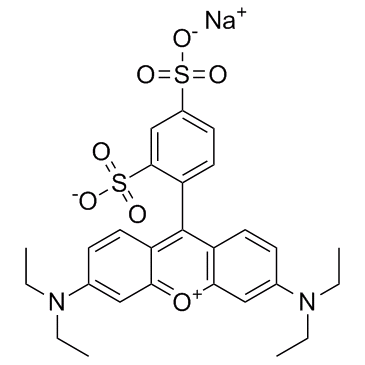 |
Acid Red 52
CAS:3520-42-1 |
|
 |
Chloramphenicol
CAS:56-75-7 |