| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
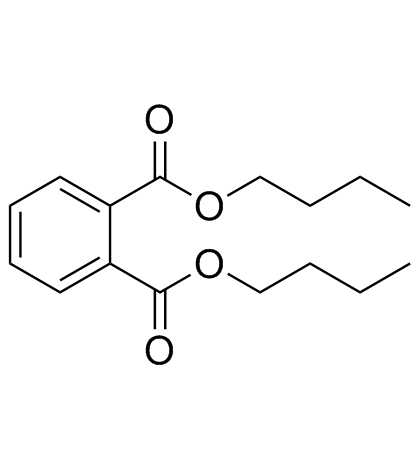 |
1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid
CAS:84-74-2 |
|
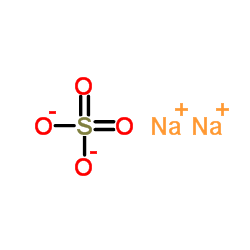 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Pyrogallol
CAS:87-66-1 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
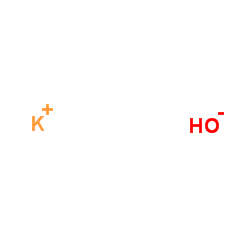 |
Potassium hydroxide
CAS:1310-58-3 |
|
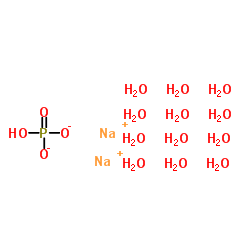 |
Disodium phosphate dodecahydrate
CAS:10039-32-4 |