| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Potassium
CAS:7440-09-7 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
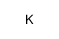 |
potassium hydride
CAS:7693-26-7 |
|
 |
E-4031
CAS:113559-13-0 |
|
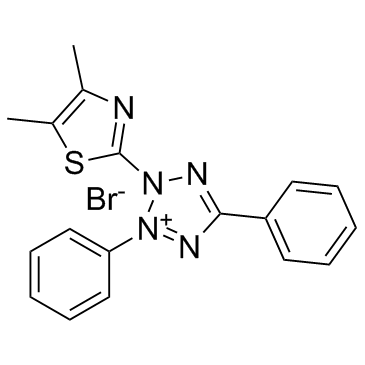 |
Thiazolyl Blue
CAS:298-93-1 |
|
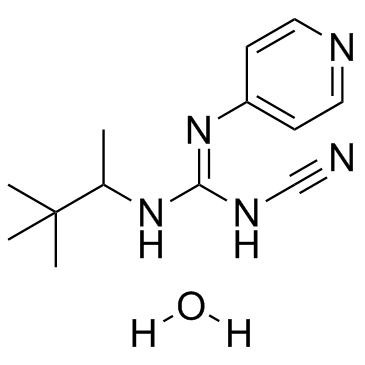 |
Pinacidil hydrate
CAS:85371-64-8 |